
Holiday Yule Log App Constantly Bombards User With Ads for Premium Version
Happy holidays!The post Holiday Yule Log App Constantly Bombards User With Ads for Premium Version appeared first on Futurism.
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.

Know what the Bible says and understand why it matters with the fully revised NIV Study Bible featuring updated notes, full-color design, and Comfort Print typography designed for immersive reading.
A trusted companion for deep personal study, sermon prep, and devotional reading highlighted in our faith and leadership coverage.

Happy holidays!The post Holiday Yule Log App Constantly Bombards User With Ads for Premium Version appeared first on Futurism.

It's not that unusual for a 20-something to text Mom from the doctor's office for help answering a health question. Or for patients of any age to struggle at recalling all their medicines. Getting the most out of a doctor's...

The U.S. reportedly plans to overhaul the country’s childhood vaccine schedule. The move could set public health back decades, experts say
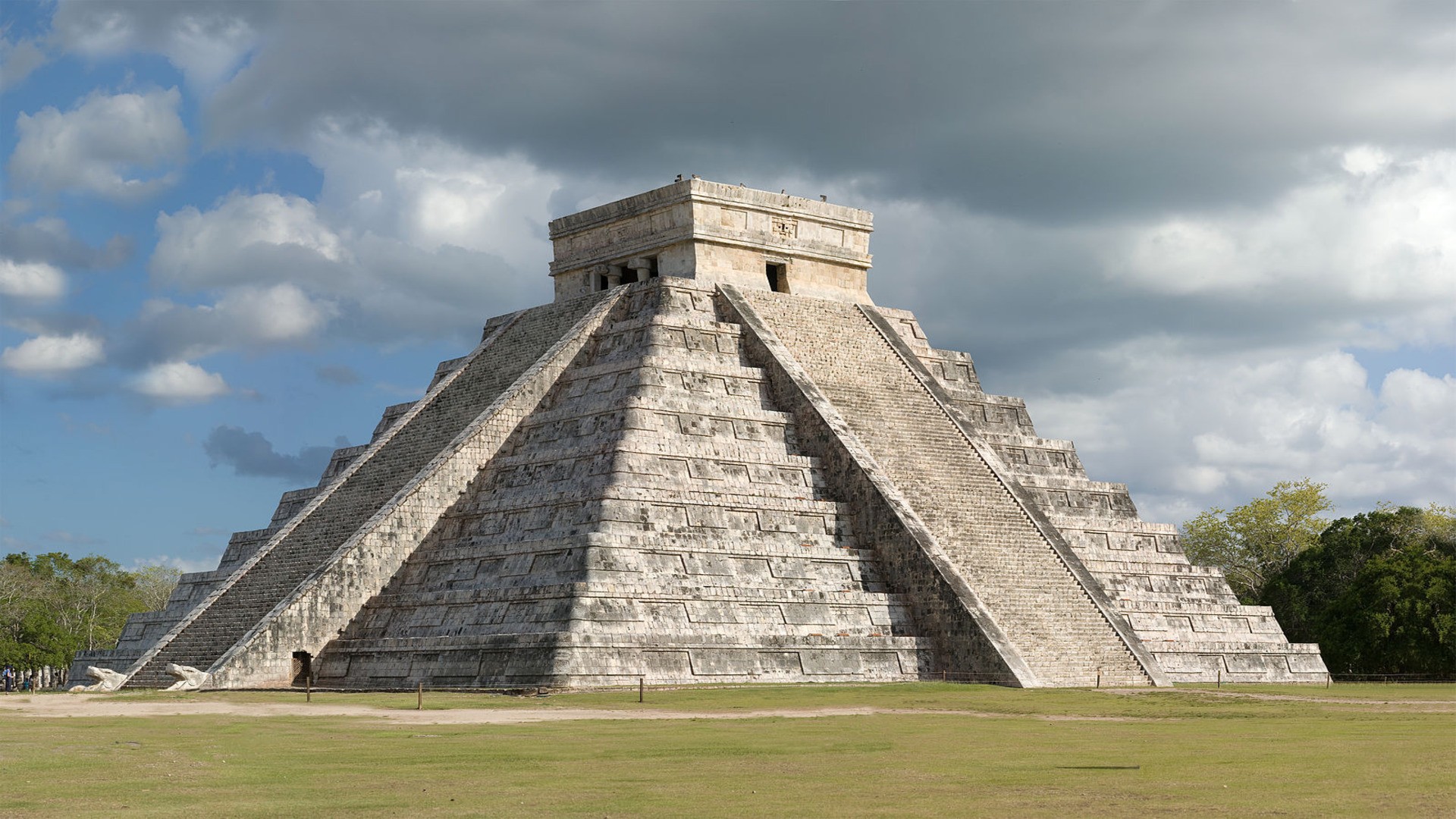

Using naturally occurring muons, researchers are embarking on a non-invasive quest to scan the interior of El Castillo.

ZIM Integrated Shipping Services (NYSE:ZIM – Get Free Report) was upgraded by research analysts at Fearnley Fonds from a “strong sell” rating to a “hold” rating in a research note issued on Friday,Zacks.com reports. Several other research analysts have also commented on the stock. Weiss Ratings reaffirmed a “hold (c)” rating on shares of ZIM [...]

AeroVironment (NASDAQ:AVAV – Get Free Report) was upgraded by research analysts at KeyCorp to a “strong-buy” rating in a research report issued to clients and investors on Thursday,Zacks.com reports. AVAV has been the subject of a number of other research reports. Needham & Company LLC reiterated a “buy” rating and set a $450.00 target price [...]
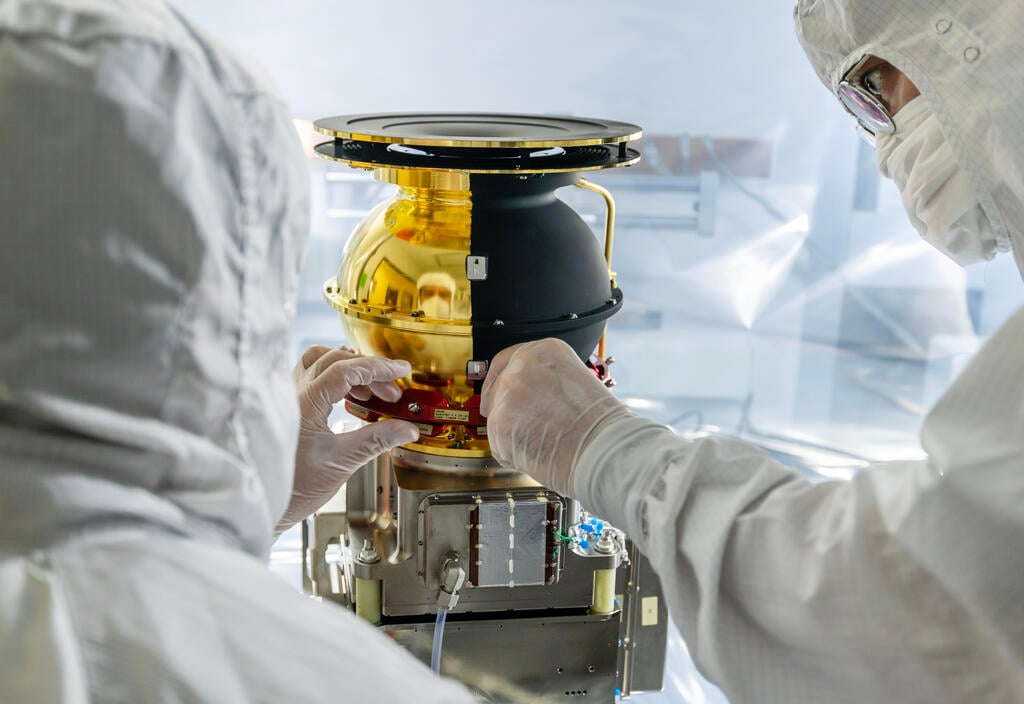

During the deployment of new space telescopes that are several critical steps each has to go through. Launch is probably the one most commonly thought of, another is “first light” of all of the instruments on the telescope. Ultimately, they’re responsible for the data the telescope is intended to collect - if they don’t work properly then the mission itself it a failure. Luckily, the Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe (IMAP) recently collected first light on its 10 primary instruments, and everything seems to be in working order, according to a press release from the Southwest Research Institute who was responsible for ensuring the delivery of all 10 instruments went off without a hitch.

WAUSEON — The Ohio State University Extension Office in Fulton County will be hosting its 20th annual Corn-Soybean Day on Jan. 16 beginning at 8 a.m. at Founder’s Hall in Archbold.

The Southern Ocean is one of the most remote places on Earth, but that doesn't mean it is tranquil. Tumultuous waves that can swallow vessels ensure that...
A new study shows that marine bacteria that alter their surfaces to avoid viral infection are still able to capture and sink carbon to the ocean floor thanks to the mutations giving the cells a "sticky" quality.
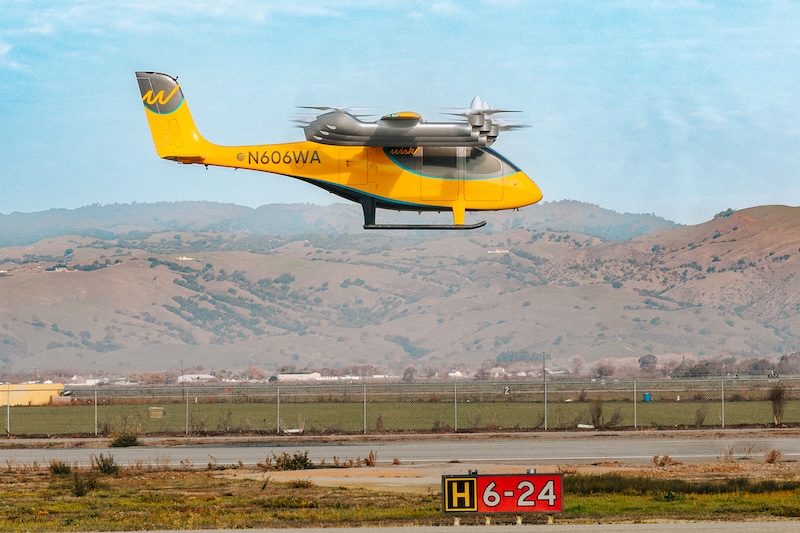

Wisk Aero, an autonomous aviation company, has announced the successful completion of the first flight of its Generation 6 aircraft. The flight is a pivotal step forward in Wisk’s journey to deliver the first certified, autonomous passenger-carrying eVTOL to market in the US Wisk says it is the only company to have designed, built, and [...]
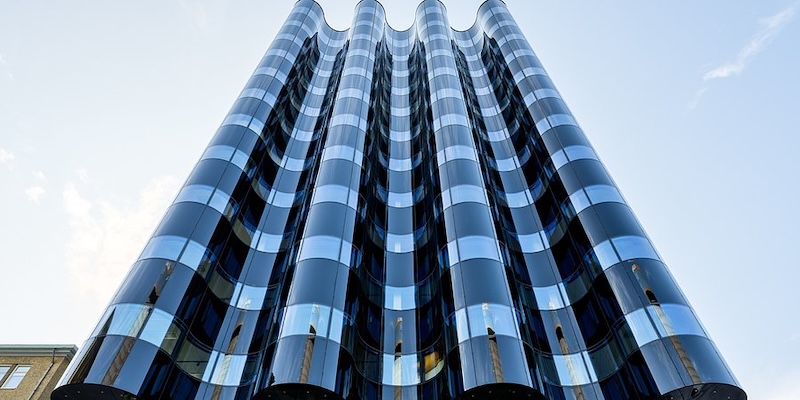

The glass industry is entering a new era of digital precision as a result of an EU-funded DiMAT project, which is helping companies like Hegla-Hanic transform complex production processes into more sustainable operations efficiently driven by data. As demand grows for spectacular glass façades and free-formed 3D designs in modern architecture, like the Vaghuset Business [...]

This batch of satellites will populate what the SDA calls the Tracking Layer of its Proliferated Warfighter Space Architecture (PWSA) constellation in low Earth orbit. The work will be divided evenly, with each company building 18 spacecraft.

A number of research firms have changed their ratings and price targets for Emergent Biosolutions (NYSE: EBS): 12/16/2025 – Emergent Biosolutions had its “buy” rating reaffirmed by analysts at HC Wainwright. They now have a $15.00 price target on the stock. 12/15/2025 – Emergent Biosolutions had its “hold (c-)” rating reaffirmed by analysts at Weiss [...]
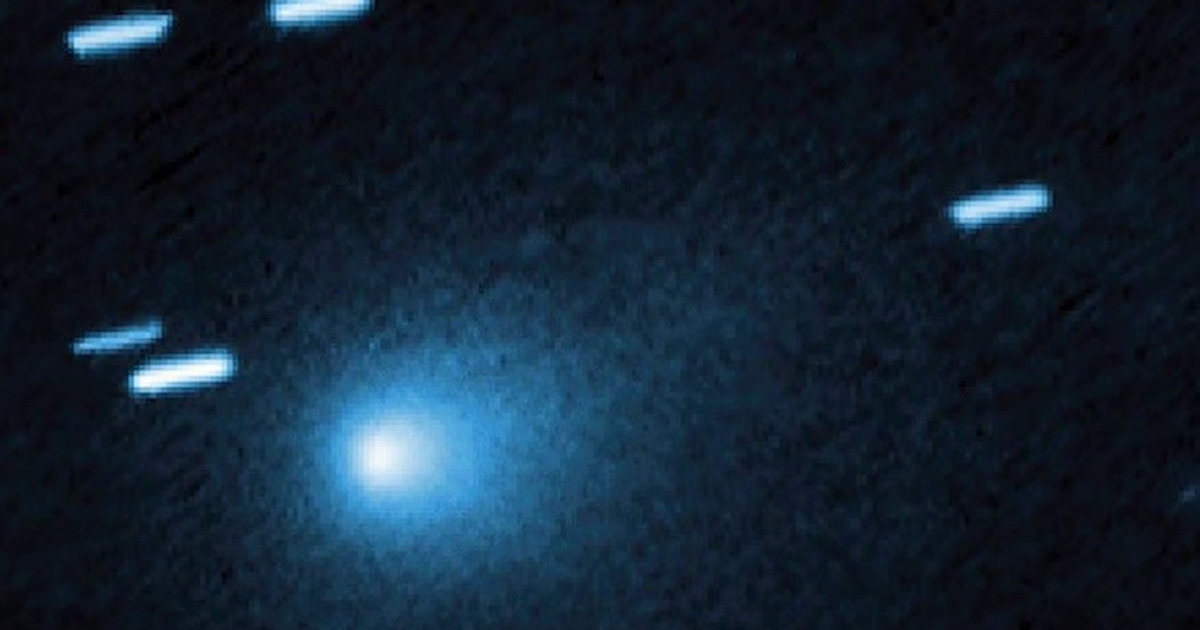

NBC News' Gadi Schwartz reports on "3I/ATLAS," a mysterious outer space object that is thought to be billions of years old, making its closest approach to Earth, giving scientists an opportunity to study it before it travels further away.
The Trump administration has awarded a $1.6 million, no-bid contract a Danish university to study hepatitis B vaccinations on newborns in Africa. The unusual contract has been awarded to scientists who have been cited by anti-vaccine activists and whose work...

Without AI buildout, U.S. GDP growth will be significantly lower. Some have said almost all of our positive GDP is from AI.
Without AI buildout, U.S. GDP growth will be significantly lower. Some have said almost all of our positive GDP is from AI.

Economic activity continues higher while market psychology remains overly dismal.

Without AI buildout, U.S. GDP growth will be significantly lower. Some have said almost all of our positive GDP is from AI.

Scientists map how quantum computer errors persist and link over time, revealing hidden memory that could reshape error correction.
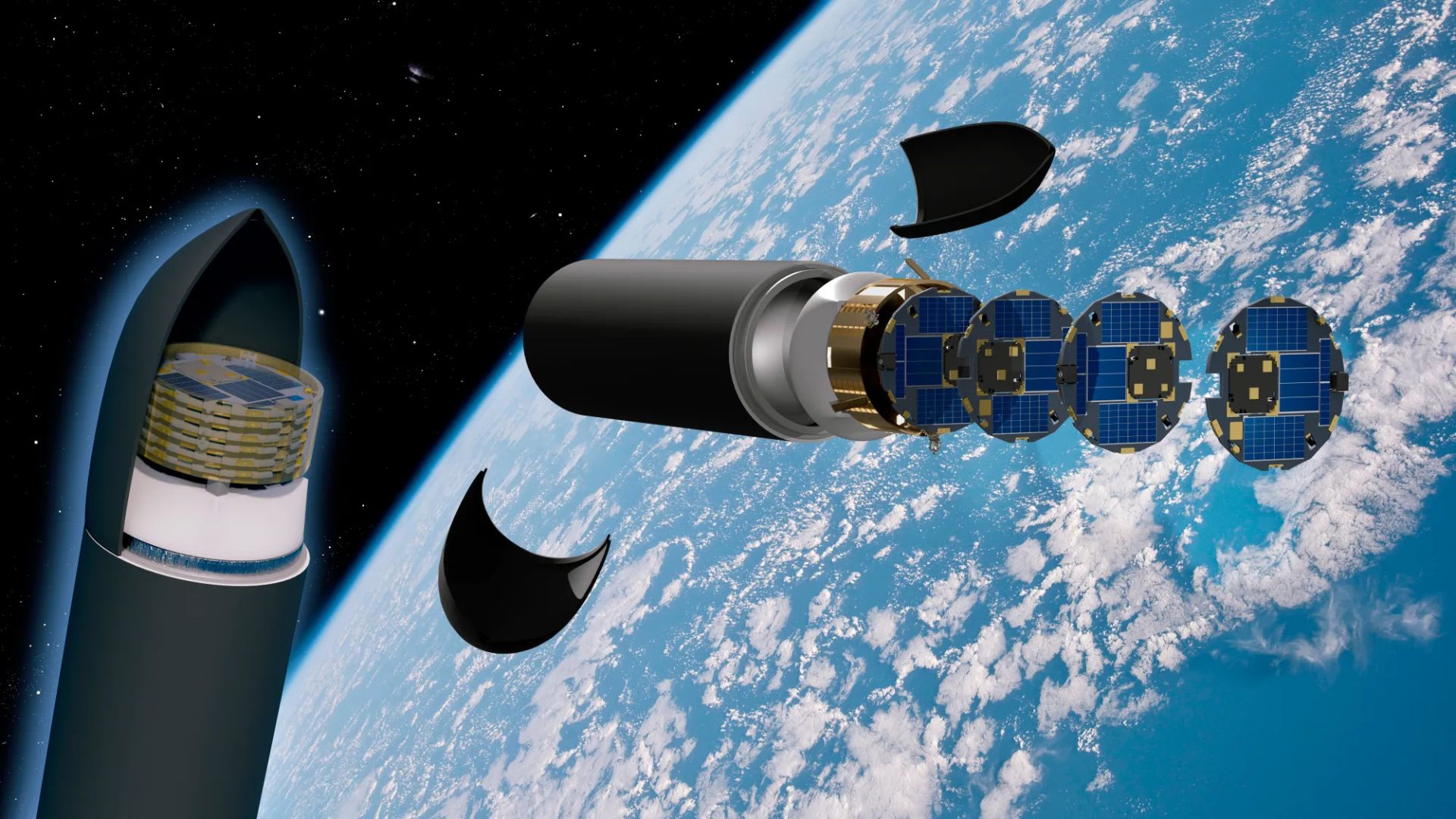

NASA's DiskSat mission is testing disk-shaped satellites in low Earth orbit, targeting sharper Earth imaging and cheaper small missions.
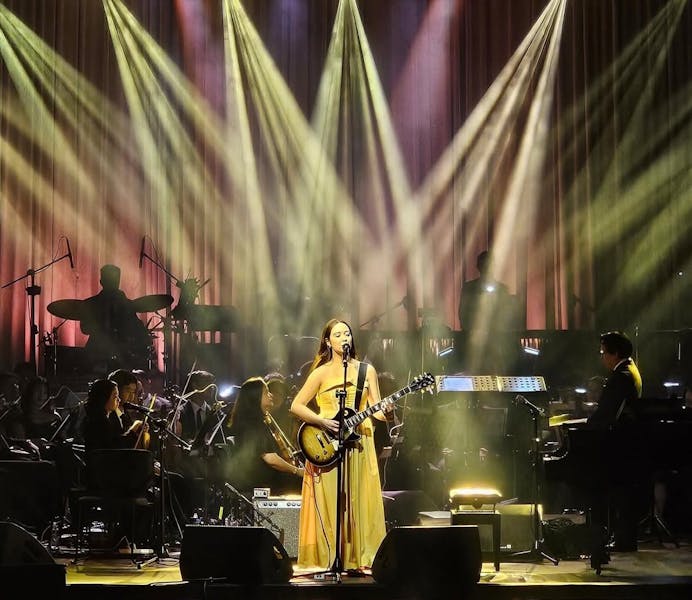

What makes a good concert?I argue that the true magic of a live performance - and of music as a whole - is intimacy. A sense of community in a sea of thousands, closeness between artist and audience that transcends the barrier between seating and stage. And somehow, on her very first arena tour for her newest album, "A Matter of Time," Laufey created that magic, translating the intimacy I feel when listening to her music into a live performance that enchanted her audience.Laufey opened her set with "Clockwork," immediately setting the tone for the rest of her concert. The first "ding-dong" of a bell tolling transported me to a world tethered between the youth of giggly first loves and the mature self-awareness of knowing what it's like to fall for someone new. The light, bossa nova rhythms behind the lyrics were even more prominent live. I couldn't help but tap my feet as I sang along.The next two songs replicated a similar airy, jazzy vibe - "Lover Girl" with its romantic, bouncy chorus and iconic claps was followed by the biting, bittersweet lyrics of "Dreamer." The song's final lines, "No boy's going to kill the dreamer in me," segued seamlessly into the melancholy of the next song, "Falling Behind."But the true magic emerged in songs that showcased Laufey's dynamic vocal range. Slow in build-up, but almost cinematic in the choruses and bridges, they had the audience holding up flashlights in awe. Reader, if you haven't experienced singing "When you go to hell, I'll go there with you too" or angry-screaming the choruses of "Too Little, Too Late" with a crowd of a thousand people wearing white skirts and ribbons, you should. There is no better catharsis and no stronger bond of affection than the one between complete strangers who like the same music.By far the best part of the night was the jazz set (during Act II), and in my opinion, it is what truly "cast a spell" during the concert. Jazz is intimate in its design because it is founded on improvisation. It is complex and unpredictable; it ebbs and flows and draws on the artist's mood on any given day - and the inclusion of a jazz set in the Laufey concert was no different. There is a comfort in knowing that no one except for the people in the arena that night heard this specific version of the songs she performed that day; it is a unique closeness, a shared experience that cannot be replicated. And for someone who'd already seen her once on the Bewitched tour, the unique flavor to the performance of "Valentine" and "While You Were Sleeping" felt like I was hearing these songs for the very first time.Acts III and IV kept the magic going, focusing almost entirely on Laufey's newest album, with a few hits from Bewitched. "Carousel," the first song of this concert's second half, defines the feelings I associate with the rest of the concert: carefree, nostalgic, almost daydream-like. My personal favorites were "Mr. Eclectic" (the perfect balance between sass and bitterness) and "Castle in Hollywood" (a wistful musing on losing friends and growing old). The playfulness continued even through songs such as "Tough Luck," where I got to see Laufey spinning on the clock-like portion of the stage during one of the most iconic bridges of the whole album.Her spell never subsided, and that feeling of specialness came back during the surprise song, "Questions for the Universe," off Everything I Know About Love (Deluxe Edition). I hadn't heard the song in years, and listening to it with just Laufey and a piano was almost enchanting. It was the perfect segue into her final song of the night, "Letter To My 13 Year Old Self," a poignant epistolary to her childhood self, with lyrics that soothed my own insecurities.After attending Laufey's Philadelphia concert, I was left with the same feeling I experienced after the first time I saw her in D.C. during the Bewitched tour: love, loss and, above all, the desire to wear an ornate ballgown and experience life through a movie screen.

CNBC’s “Fast Money” team shares their final trades of the day.

CNBC’s 75 most valuable college athletic programs for 2025 are worth a combined $51.22 billion. The "Fast Money" team is joined by senior sports reporter Mike Ozanian and Jason Belzer, publisher of the Athletic Director U to break down the numbers.

CNBC's "Fast Money" team discusses the tech trade, the future of AI, data center demand and more with Rick Sherlund, senior advisor at Wedbush.

NASA opens the International Space Station for scientists and researchers, inviting them to use the benefits of microgravity for private industry research, technology demonstrations, and more. Today, half of the crew's time aboard station is devoted to these aims, including medical research that addresses complex health challenges on Earth and prepares astronauts for future deep space missions.

A scientific experiment aimed at detecting dark matter in space launched from Antarctica on December 15, with significant contributions from University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa.

Through a novel combination of machine learning and atomic force microscopy, researchers in China have unveiled the molecular surface structure of "premelted" ice, resolving a long-standing mystery surrounding the liquid-like layer which forms on icy surfaces.

Behind every particle collision generated at the Large Hadron Collider is a multitude of technical feats. One of these is refrigeration on an industrial scale. To guide the particles, the thousands of superconducting magnets in the accelerator must be cooled to a temperature of close to absolute zero. This makes the LHC the largest cryogenic installation in the world: 23 of its 27 kilometers are maintained at 1.9 Kelvin (-271°C) using refrigerators in which superfluid helium circulates.

Even when information is factually accurate, how it’s presented can introduce subtle biases. As large language models increasingly bring people the news...
Some of the wealthiest individuals in technology including Eric Schmidt and France’s Xavier Niel have pledged as much as €860 million ($1 billion) to CERN to fund a proposed successor to the Large Hadron Collider, as the storied research institute turns to private backers for the first time to back future breakthroughs.

While the spread of raccoons in Europe is often discussed, their companion tends to remain unnoticed: The raccoon roundworm Baylisascaris procyonis arrived in Europe at the beginning of the 20th century with the first raccoons from North America.
TORONTO, Dec. 19, 2025 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Xanadu Quantum Technologies Inc. ("Xanadu"), a leading photonic quantum computing company, today announced that it has developed a novel quantum computational framework to accelerate the discovery of next-generation photosensitizers for photodynamic cancer therapy, a targeted cancer treatment. Published as a pre-print article on arXiv, Xanadu's new research demonstrates how fault-tolerant quantum computers can accelerate research into cutting-edge cancer treatments.Photodynamic cancer therapy uses light-activated compounds called photosensitizers to selectively destroy tumor cells, typically resulting in less collateral damage than conventional treatments, such as chemotherapy. However, a photosensitizer's success or failure often depends on complex properties, such as sensitivity to specific wavelengths of light and efficiency in triggering cancer cell death. Through the application of quantum simulation algorithms to four diverse photosensitizers, several of which are particularly challenging for classical simulations, Xanadu's new research shows that quantum computers can effectively simulate the key properties needed to model and improve these treatments."The development of effective photosensitizers is currently hampered by the high cost and runtime required for experimental synthesis and classical simulations. We believe our results position fault-tolerant quantum computing as a highly attractive solution for discovering advanced photosensitizers by modelling key physical properties," says Christian Weedbrook, Founder and Chief Executive Officer of Xanadu.Through this work, Xanadu provides a blueprint for an efficient, quantum-based workflow that can help identify potentially promising drug candidates. By focusing on simulating critical physical properties, such as cumulative absorption and intersystem crossing rates, Xanadu provides a way to determine, from first principles, which photosensitizer candidates could lead to highly efficient generation of reactive, cancer-killing molecules, thereby supporting the effectiveness of the photodynamic cancer treatment. In addition, the research provides estimates for the computational resources required to run these algorithms on utility-scale quantum computers and indicates potential speed and efficiency gains over classical methods.This research serves as a foundational step toward a quantum-based workflow for drug design, with additional work planned to extend the framework to model more complex photosensitizer molecules. It provides an exciting new avenue for quantum computing to push the boundaries of drug development and cancer treatment.Business CombinationXanadu recently announced a business combination agreement with Crane Harbor Acquisition Corp. (NASDAQ:CHAC), a publicly traded special purpose acquisition company ("Crane Harbor"). The combined company, Xanadu Quantum Technologies Limited ("NewCo"), is expected to be capitalized with approximately US$500 million in gross proceeds, comprising approximately US$225 million from Crane Harbor's trust account, assuming no redemptions by Crane Harbor's public stockholders, as well as US$275 million from a group of strategic and institutional investors participating in the transaction via a common equity committed private placement investment. NewCo is expected to be listed on the Nasdaq Stock Market and on the Toronto Stock Exchange.About XanaduXanadu is a Canadian quantum computing company with the mission to build quantum computers that are useful and available to people everywhere. Founded in 2016, Xanadu has become one of the world's leading quantum hardware and software companies. Xanadu also leads the development of PennyLane, an open-source software library for quantum computing and application development. Visit xanadu.ai or follow us on X @XanaduAI.About Crane HarborCrane Harbor is a blank check company formed for the purpose of effecting a merger, share exchange, asset acquisition, share purchase, reorganization or similar business combination with one or more businesses.Additional Information About the Proposed Transaction and Where to Find ItThe proposed business combination transaction will be submitted to shareholders of Crane Harbor and Xanadu for their consideration. NewCo and Crane Harbor have jointly confidentially submitted a draft registration statement on Form F-4 (the "Registration Statement") to the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (the "SEC"). The Registration Statement includes a proxy statement/prospectus to be distributed to Crane Harbor's shareholders in connection with Crane Harbor's solicitation of proxies for the vote by Crane Harbor's shareholders in connection with the proposed transaction and other matters to be described in the Registration Statement, as well as the prospectus relating to the offer of the securities to be issued to Xanadu's shareholders in connection with the completion of the proposed transaction. After the Registration Statement has been publicly filed and declared effective by the SEC, a definitive proxy statement/prospectus and other relevant documents will be mailed ...Full story available on Benzinga.com

Long before scientists discovered that other stars in the universe host their own planetary systems, humanity had contemplated the existence of life beyond Earth. As our technology matured and we began monitoring the night sky in multiple wavelengths (i.e., radio waves), this curiosity became a genuine scientific pursuit. By the 1960s, a scientific field dedicated to the search for advanced life (similar to ours) emerged: the Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI). Since then, multiple SETI surveys have been conducted to search for potential signs of technological activity (aka "technosignatures").

Philippine scientists and an Australian expert have just confirmed a new species of pitcher plant found only on Palawan Island, but warn that it is already at risk of extinction due to frequent severe weather conditions and human encroachment.

New vaccines that display filovirus surface proteins on engineered, self-assembling protein nanoparticles can improve immune system detection of the virus. The nanoparticles triggered strong antibody responses across several filoviruses in mice, highlighting a promising path toward viral protection. The post Filovirus Detection by Immune System Improved by Nanoparticle Vaccine appeared first on GEN - Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology News.
(MENAFN - EIN Presswire) EINPresswire/ -- Researchers are exploring whether dentists may one day use stem cells to help grow new teeth. While this idea once sounded out of reach, new studies show ...
Researchers are developing ultra-fast, brain-inspired chips that could cut AI energy use in data centers while boosting computing speed.

A man with a knife and smoke grenades attacked crowds indiscriminately in Taiwan's capital on Friday evening, killing at least three people and injuring nine others, according to the national news agency and the city government. The suspect later fell to his death from a department store building. Police said...

By studying drinking in a controlled social environment, CMU researchers can learn how drinking unfolds in real time between people — an innovative approach that brings the rigor of the lab closer to the authentic social contexts where alcohol use usually occurs.

Many biological processes are regulated by electricity—from nerve impulses to heartbeats to the movement of molecules in and out of cells.
(MENAFN - Investor Brand Network)Annovis Bio (NYSE: ANVS) announced it will initiate an open-label extension study in January 2026 to further evaluate the long-term safety and efficacy of ...

University of Victoria (UVic) biologists have discovered that even closely related fish species make unique and distinctive sounds and determined that it's possible to differentiate between the sounds of different species. The discovery opens the door to identifying fish based on sound alone.

The recent delivery of advanced nuclear fuel to the Idaho National Laboratory's Transient Reactor Test Facility marks a major milestone for Project Pele, a first-of-its-kind mobile microreactor prototype designed to provide resilient power for military operations.

The Idaho National Laboratory today announced initial selections for the Microreactor Application Research Validation and Evaluation (MARVEL) end user experiments.

An unusual object orbiting a rapidly spinning star might be a new phenomenon in the universe.

In recent years, members of the Canadian public have witnessed the misrepresentation of Indigenous identities.

Anyone seeing a white jacaranda (Jacaranda puberula), also known as caroba, blooming in the sandbank forest might assume that the leafy tree could not survive in such sandy soil. They would be right. This type of Atlantic Forest, located very close to the sea, is characterized by species that thrive in acidic soil with few nutrients.

With a new method that could be extended to study Earth's core and nuclear fusion, they identify and explain jumps in the electrical conductivity of aluminum under extreme conditions.

Over the course of this year, the dedicated scientists, engineers, technicians and operations staff at Fermilab came together to drive discoveries that shape the future of particle physics, utilize their experience and expertise to drive American innovation and prepare the lab for a bright future.

In a study published in Nature Communications, a team of researchers developed a new approach that can isolate biomarkers released from glioblastoma tumor cells.They showed that their method can be used to determine the effectiveness of the chemotherapy drug paclitaxel.

UCLA has been awarded a $7.5 million grant from Aligning Research to Impact Autism to support the Innovative Medicine and Precision Approaches to Clinical Trials Network, which focuses on autism and related neurodevelopmental conditions.
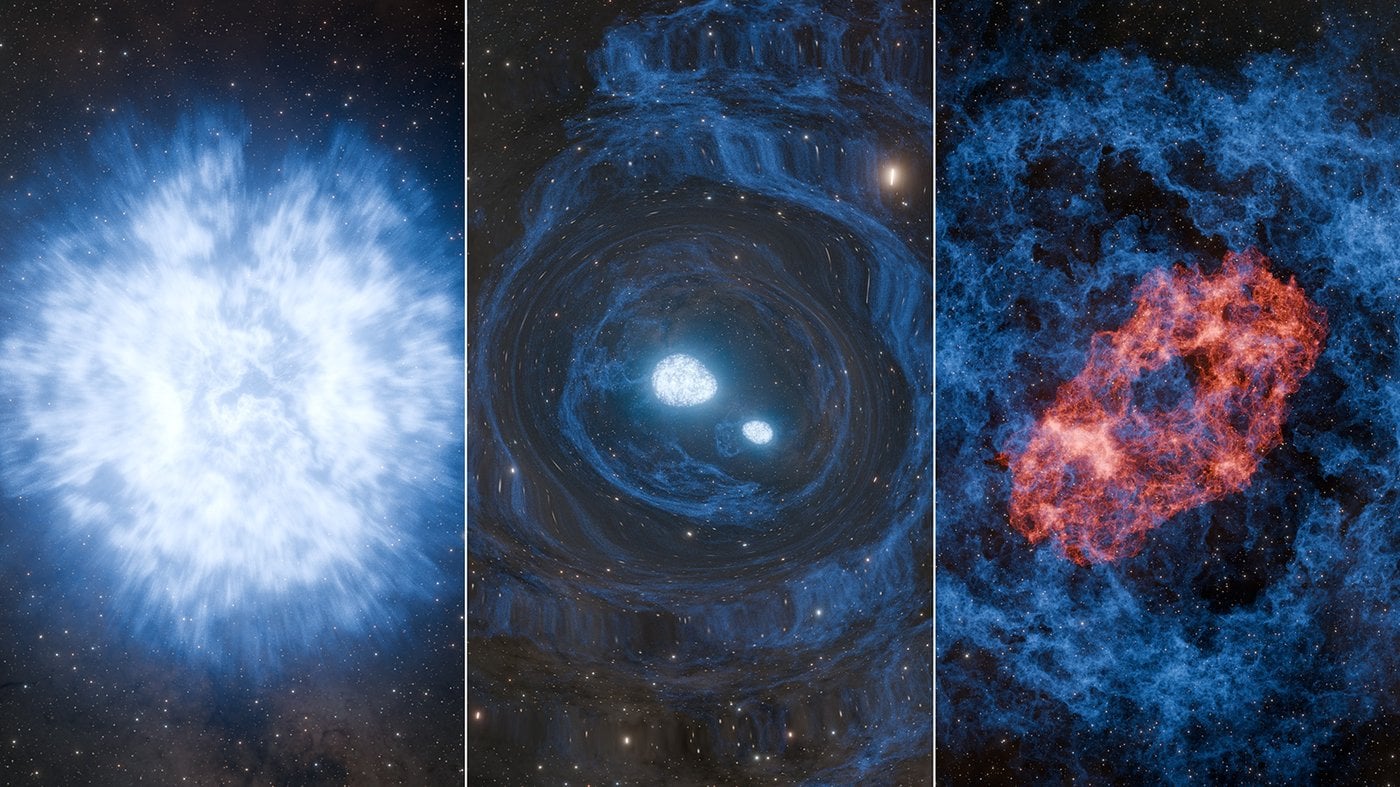

Astronomers may have just seen the first ever ‘superkilonova,’ a combination of a supernova and a kilonova. These are two very different kinds of stellar explosions, and if this discovery stands, it could change the way scientists understand stellar birth and death.

Armando Falcon-Brindis has noticed a few newcomers buzzing around University of Idaho’s Parma Research and Extension Center ever since he helped build a garden of flowering plants to accommodate pollinators.

Scientists at University of Idaho’s Parma Research and Extension Center recently showcased their state-of-the-art new laboratory during a unique training that attracted crop pest and disease diagnosticians from throughout the country.

Tired of AI customer service loops? These insider tricks help you escape "frustration AI" and get real human help when you need it most for urgent issues.

From fruit flies that bite to a tiny mouse opossum and a feathered dinosaur preserved with the remains of its last meal, more than 70 new species were described this year by researchers at the American Museum of Natural History.

Engineered dendritic cells with EV‐internalizing and chimeric antigen receptors capture tumor vesicles, activate T cells, and delay melanoma growth in preclinical models, advancing next‐generation cancer immunotherapy strategies.The post Engineered Dendritic Cells Harness Tumor EVs to Boost Cancer Immunotherapy appeared first on GEN - Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology News.

Scientists at St. Jude Children's Research Hospital described for the first time a short-lived kinase state that is essential for normal cell migration and T-cell function.

Mountain permafrost is warming and thawing worldwide due to climate change, with ground temperature being a key control of its mechanical stability. Heat conduction is the dominant mode of heat transfer in frozen ground, and thermal diffusivity governs the rate at which temperature changes propagate through the subsurface. Despite its relevance, there are few field-based estimates of thermal diffusivity.
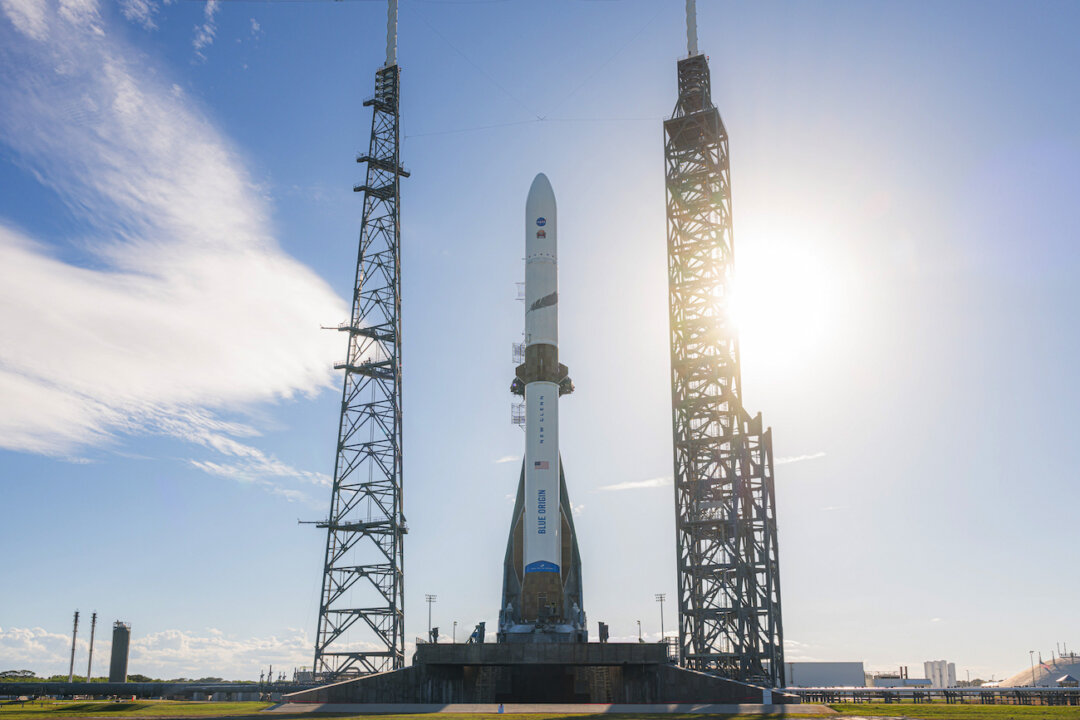

The president said he would prioritize the nation’s push to space for commercial, national security, and exploration purposes.

Shandin Pete, a Salish and Navajo hydrogeologist and science educator, talks about Salish constellations and why Indigenous astronomy is important.
ZHUHAI, China, Dec. 18, 2025 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Rezubio, a China-based biotechnology company founded by former Merck scientists, today announced the closing of a $20 million Series A financing. Proceeds will be used to advance the company's lead program into Phase 2 clinical development for obesity and diabetes, as well as other programs in IND-enabling stage and early preclinical stage.The financing was led by Lapam Capital, with participation from Frees Fund and Riverhead Capital."This Series A represents an important inflection point for ...Full story available on Benzinga.com

Science can be as dynamic as the researchers who explore it. The Society of Asian Scientists and Engineers is recognizing three Sandia National Laboratories engineers who pushed beyond the boundaries of linear research to expand their knowledge and impact across multiple fields.

When the world slowed down during the COVID-19 pandemic, its effects extended beyond humans. A recent study found that it reshaped urban ecosystems to such an extent that certain city-dwelling birds even began to develop longer, thinner beaks resembling those of their wild relatives.

Every year since 2010, I’ve posted an article about what trend I expect to dominate the next twelve months. Throughout the 2010s, these forecasts usually focused on emerging technologies or new currents in management thinking. But around 2020, that began to shift. The annual trends increasingly centered on how we cope with change rather than the change itself.Last year my trend was “The Coming Realignment.” History tends to propagate at a certain rhythm and then converge and cascade around certain points. Years like 1776, 1789, 1848, 1920, 1948, 1968, 1989—and, it seems, 2020—mark these inflection points. The years that follow are usually spent absorbing the shock and navigating the consequences. Today, everything is up for question. Will AI boom or bust? Will it take our jobs or bring new prosperity? What kind of economic system will we adopt for the future? We are in the midst of a great realignment. What we know from previous inflections is that what comes after will be profoundly different from before. What we most need to watch is our institutions.AI boom or bust?Today, the AI investment boom is without a doubt the single biggest factor propping up the US economy. Just this year, tech giants are expected to invest roughly $364 billion in the technology. And the spending won’t stop there. McKinsey projects that building AI data centers could add up to $5.2 trillion in investment by 2030.This boom is different from what we’ve seen in the past because the main investors aren’t speculators or startups, but some of the world’s most profitable companies, including Alphabet, Meta, and Microsoft. Unlike in past cycles, if the industry hits a downturn, there will still be tens of billions of dollars in annual profits to cushion the blow. Still, as investor Paul Kedrosky points out, there are reasons to worry. Investment in data center infrastructure has already surpassed the peak of the dot-com boom and is beginning to approach levels last seen during the railroad frenzy of the 19th century. Also, 60% of the cost of those data centers goes to AI chips, which have a useful life of only about three years.That means this is not a boom that can wait decades to pay off. If today’s investments don’t generate returns in the near future, much of the infrastructure could fully depreciate before delivering meaningful profit. In practical terms, unless tech firms can earn more than $200 billion in profit—on these investments alone, not from their core businesses—they will be underwater. And as investment accelerates, that bar only rises.Kedrosky also notes signs of growing systemic risk. Increasingly, tech giants are choosing to finance their infrastructure build-outs with Enron-like special-purpose vehicles. These structures cost more but keep the debt off their balance sheets. That risk, in turn, is increasingly being passed to more traditional investors, including REITs.Will AI displace humans or enhance us? A 2023 report by the World Economic Forum, analyzing 673 million jobs, predicted structural job growth of 69 million jobs and a decline of 83 million, an overall decrease of 14 million jobs. An IMF analysis found that 40% of global employment is exposed. In an interview with Axios, Anthropic CEO Dario Amodei said AI could wipe out half of all entry-level white-collar jobs in the next one to five years.Yet more grounded economic analyses suggest a much more modest impact. A study by the St. Louis Fed suggests a 1.1% increase in aggregate worker productivity, with much of that increase concentrated in the tech sector. A paper by Nobel laureate Daron Acemoglu, which looks at total factor productivity (TFP), a measure which takes use of capital into account, sees a 0.66% increase over 10 years, translating to a 0.064% increase in annual TFP growth.A recent McKinsey report takes an optimistic view. While noting that many routine office and production jobs are likely to disappear, those that leverage technical, social and emotional skills are likely to flourish, just as Autor has predicted. However, there is reason to suspect that optimists may be merely extrapolating from historical trends that may no longer apply.There’s no guarantee that the future will look like the past. An analysis in Harvard Business Review suggested that AI could disrupt the non-routine creative work that, to this point, has been hard to automate. Meanwhile, research in Science has found that, although AI may enhance individual creative work, it diminishes the diversity of novel output, potentially stifling the very innovation it aims to support.What will be the economic system of the future? Before 1789 the world was ruled by the divine right of kings and the feudal system. Yet that year would prove to be an inflection point. The American Constitution, the French Revolution, and the first Industrial Revolution, already underway since the introduction of the steam engine in 1776, together created a fundamental realignment of power.These forces would build and clash for decades until things came to a head in the revolutionary year of 1848. Today, we seem to be in a similarly liminal space, as we decide what kind of future we want to live in. The next century and a half would be dominated by the tensions between socialism and capitalism. When the Berlin Wall came down in 1989, the West was triumphant. Communism was exposed as a corrupt system bereft of any real legitimacy. Yet for anyone paying attention, communism had long been discredited. As far back as the 1930s, Stalin’s disastrous collectivization and industrialization campaigns had led to mass starvation. By the 1970s, Soviet total factor productivity growth had gone negative, meaning more investment actually brought less output. Yet today, it is capitalism that finds itself under siege from all sides. Leftist progressives like Bernie Sanders and Zohran Mamdani advocate for reining in the private sector and creating a bigger safety net. The mercantilist American president rails against free trade and nationalizes the means of production. Christian nationalists openly call for theocratic rule.At the same time, a new cadre of theorists has emerged whose ideas don’t fit the traditional right-left paradigm. New Right thinkers such as Curtis Yarvin and Patrick Deneen call for wholesale reordering of society. On the more technocratic side, a new school of thought is emerging that is associated with Ezra Klein and Derek Thompson’s book Abundance.It’s the institutions, stupidIn Why Nations Fail, economists Daron Acemoglu and James Robinson explain why the fate of nations rests less on innate factors such as geography, culture, or climate and more on the quality and types of institutions they build. In particular, they make the distinction between inclusive institutions and extractive institutions. Inclusive institutions protect property rights broadly across society, establish fair competition, and reward innovation. Extractive institutions, on the other hand, concentrate wealth in the hands of a small elite who exploit the broader population. These elite players control resources and use state power to enrich themselves at society’s expense.We are clearly in a liminal period in which we are struggling to adapt to shifts in technology, economics, and identity. Will AI oppress or empower regular people? Will we trade openly or retreat behind national barriers? Will we focus primarily on our local communities or see ourselves as citizens of a larger planet? As ever, there will be no shortage of pundits predicting the paths the future will take. Many of their narratives will be persuasive—but also mutually contradictory. The real tell will be what kinds of institutions we build and which ones we allow to decay or be destroyed outright. Are we creating institutions that strengthen rights and the rule of law, or those that serve the powerful?The outcome is still unclear, but the lines of battle have been drawn. If you want to know what to expect in the near to mid-term, pay less attention to predictions about technology, politics, or ideology and focus instead on institutions. Those are what create the norms and rituals that will shape the behaviors of the future.

The Syrian civil war, which began in 2011, has been widely framed as a "climate conflict" and a mass migration and uprising triggered by a severe drought. This very well-known and media-popular narrative is now debunked in a new report by the United Nations University Institute for Water, Environment and Health (UNU-INWEH).

One of the researchers said that the findings are especially relevant in high-stakes contexts like eyewitness testimony.
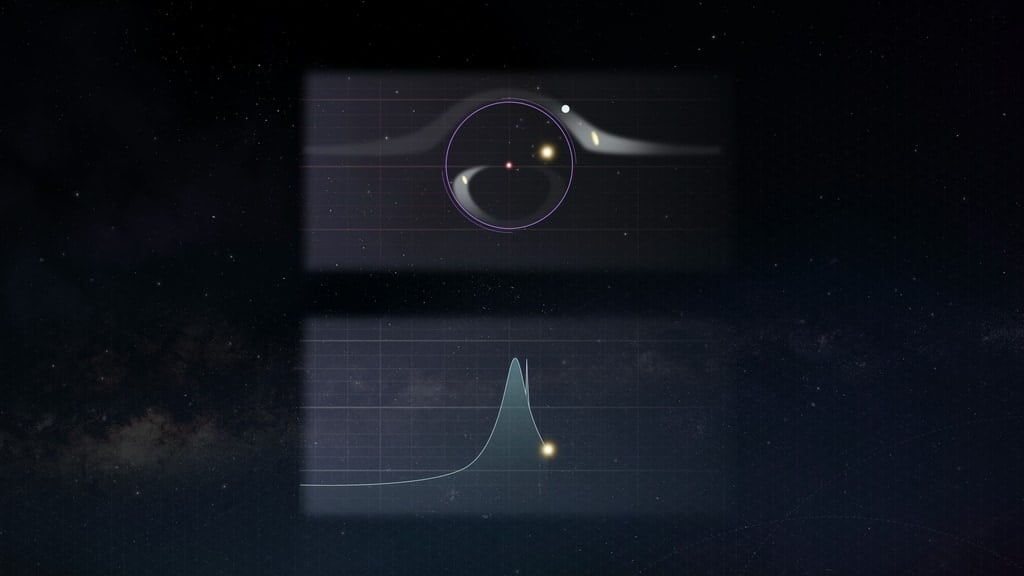
With new technologies comes new discoveries. Or so Spider Man’s Uncle Ben might have said if he was an astronomer. Or a scientist more generally - but in astronomy that saying is more true than many other disciplines, as many discoveries are entirely dependent on the technology - the telescope, imager, or processing algorithm, used to collect data on them. A new piece of technology, the Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope, is exciting scientists enough that they are even starting to predict what kind of discoveries it might make. One such type of discovery, described in a pre-print paper on arXiv by Vito Saggese of the Italian National Institute for Astrophysics and his co-authors on the Roman Galactic Exoplanet Survey Project Infrastructure Team, is the discovery of many more multiplantery exoplanet systems an astronomical phenomena Roman is well placed to detect - microlensing.

Now divided between Romania and Ukraine, the region never fit easily among its neighbors, as regimes including the Habsburg Empire and the Soviet Union tried to remake it in their image.

Ocean Optics reports on how spectroscopy revolutionizes research by utilizing light to analyze materials, improving accuracy and efficiency.

An international research expedition involving Cornell has uncovered new details as to why a 2011 earthquake northeast of Japan behaved so unusually as it lifted the seafloor and produced a tsunami that devastated coastal communities.

New research shows the Chesapeake Bay’s top invader is hard to control.
Trump Media & Technology Group Corp., the company behind Truth Social, is getting into nuclear fusion.

Jane Dever, director of Clemson University’s Pee Dee Research and Education Center (REC) near Florence, South Carolina, has...The post Dever inducted into Cotton Research and Promotion Hall of Fame appeared first on Clemson News.

A recent NBER study, "Technology and the Innovation Shock," reveals that technological breakthroughs like AI boost GDP by 2-3% short-term and enhance productivity, but they widen income inequality by favoring capital owners and high-skilled workers while displacing routine jobs. Policymakers must implement retraining and progressive measures to ensure equitable benefits.

Gazing Into the Mind’s Eye With Mice – How Neuroscientists Are Seeing Human Vision More ClearlySuperadminThu, 12/18/2025 - 09:08 Despite the nursery rhyme about three blind mice, mouse eyesight is surprisingly sensitive. Studying how mice see has helped researchers discover unprecedented details about how individual brain cells communicate and work together to create a mental picture of the visual world.I am a neuroscientist who studies how brain cells drive visual perception and how these processes can fail in conditions such as autism. My lab “listens” to the electrical activity of neurons in the outermost part of the brain called the cerebral cortex, a large portion of which processes visual information. Injuries to the visual cortex can lead to blindness and other visual deficits, even when the eyes themselves are unhurt.Understanding the activity of individual neurons – and how they work together while the brain is actively using and processing information – is a long-standing goal of neuroscience. Researchers have moved much closer to achieving this goal thanks to new technologies aimed at the mouse visual system. And these findings will help scientists better see how the visual systems of people work.The Mind in the Blink of an EyeResearchers long thought that vision in mice appeared sluggish with low clarity. But it turns out visual cortex neurons in mice – just like those in humans, monkeys, cats and ferrets – require specific visual features to trigger activity and are particularly selective in alert and awake conditions.My colleagues and I and others have found that mice are especially sensitive to visual stimuli directly in front of them. This is surprising, because mouse eyes face outward rather than forward. Forward-facing eyes, like those of cats and primates, naturally have a larger area of focus straight ahead compared to outward-facing eyes.This image shows neurons in the mouse retina: cone photoreceptors (red), bipolar neurons (magenta), and a subtype of bipolar neuron (green). Brian Liu and Melanie Samuel/Baylor College of Medicine/NIH via FlickrThis finding suggests that the specialization of the visual system to highlight the frontal visual field appears to be shared between mice and humans. For mice, a visual focus on what’s straight ahead may help them be more responsive to shadows or edges in front of them, helping them avoid looming predators or better hunt and capture insects for food.Importantly, the center of view is most affected in aging and many visual diseases in people. Since mice also rely heavily on this part of the visual field, they may be particularly useful models to study and treat visual impairment.A Thousand Voices Drive Complicated ChoicesAdvances in technology have greatly accelerated scientific understanding of vision and the brain. Researchers can now routinely record the activity of thousands of neurons at the same time and pair this data with real-time video of a mouse’s face, pupil and body movements. This method can show how behavior interacts with brain activity.It’s like spending years listening to a grainy recording of a symphony with one featured soloist, but now you have a pristine recording where you can hear every single musician with a note-by-note readout of every single finger movement.Using these improved methods, researchers like me are studying how specific types of neurons work together during complex visual behaviors. This involves analyzing how factors such as movement, alertness and the environment influence visual activity in the brain.For example, my lab and I found that the speed of visual signaling is highly sensitive to what actions are possible in the physical environment. If a mouse rests on a disc that permits running, visual signals travel to the cortex faster than if the mouse views the same images while resting in a stationary tube – even when the mouse is totally still in both conditions.In order to connect electrical activity to visual perception, researchers also have to ask a mouse what it thinks it sees. How have we done this?The last decade has seen researchers debunking long-standing myths about mouse learning and behavior. Like other rodents, mice are also surprisingly clever and can learn how to “tell” researchers about the visual events they perceive through their behavior.For example, mice can learn to release a lever to indicate they have detected that a pattern has brightened or tilted. They can rotate a Lego wheel left or right to move a visual stimulus to the center of a screen like a video game, and they can stop running on a wheel and lick a water spout when they detect the visual scene has suddenly changed.Mice can be trained to drink water as a way to ‘tell’ researchers they see something. felixmizioznikov/iStock via Getty Images PlusMice can also use visual cues to focus their visual processing to specific parts of the visual field. As a result, they can more quickly and accurately respond to visual stimuli that appear in those regions. For example, my team and I found that a faint visual image in the peripheral visual field is difficult for mice to detect. But once they do notice it – and tell us by licking a water spout – their subsequent responses are faster and more accurate.These improvements come at a cost: If the image unexpectedly appears in a different location, the mice are slower and less likely to respond to it. These findings resemble those found in studies on spatial attention in people.My lab has also found that particular types of inhibitory neurons – brain cells that prevent activity from spreading – strongly control the strength of visual signals. When we activated certain inhibitory neurons in the visual cortex of mice, we could effectively “erase” their perception of an image.These kinds of experiments are also revealing that the boundaries between perception and action in the brain are much less separate than once thought. This means that visual neurons will respond differently to the same image in ways that depend on behavioral circumstances – for example, visual responses differ if the image will be successfully detected, if it appears while the mouse is moving, or if it appears when the mouse is thirsty or hydrated.Understanding how different factors shape how cortical neurons rapidly respond to visual images will require advances in computational tools that can separate the contribution of these behavioral signals from the visual ones. Researchers also need technologies that can isolate how specific types of brain cells carry and communicate these signals.Data Clouds Encircling the GlobeThis surge of research on the mouse visual system has led to a significant increase in the amount of data that scientists can not only gather in a single experiment but also publicly share among each other.Major national and international research centers focused on unraveling the circuitry of the mouse visual system have been leading the charge in ushering in new optical, electrical and biological tools to measure large numbers of visual neurons in action. Moreover, they make all the data publicly available, inspiring similar efforts around the globe. This collaboration accelerates the ability of researchers to analyze data, replicate findings and make new discoveries.Technological advances in data collection and sharing can make the culture of scientific discovery more efficient and transparent – a major data informatics goal of neuroscience in the years ahead.If the past 10 years are anything to go by, I believe such discoveries are just the tip of the iceberg, and the mighty and not-so-blind mouse will play a leading role in the continuing quest to understand the mysteries of the human brain. This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article. Subtitle Summary sentence Studying how mice see has helped researchers discover unprecedented details about how individual brain cells communicate and work together to create a mental picture of the visual world. Summary Studying how mice see has helped researchers discover unprecedented details about how individual brain cells communicate and work together to create a mental picture of the visual world. Dateline Tue, 12/16/2025 - 12:00 Contact Author:Bilal Haider, Associate Professor of Biomedical Engineering, Georgia Institute of TechnologyMedia Contact:Shelley [email protected] Related links Read This Article on The Conversation Associated importer 1 Keywords go-resarchnews News room topics Science and Technology Mercury ID 686983 Source updated Thu, 12/18/2025 - 08:57

British policymakers planning for climate change now have detailed worst-case scenarios at their disposal, filling a gap that left the UK unprepared for extreme outcomes.

Real skeptics study the evidence and ask questions, rather than taking political dogma on faith. Experiencing disasters can open more eyes to the risks.

(The Conversation is an independent and nonprofit source of news, analysis and commentary from academic experts.)

Water is a vital resource. Life on Earth, as we know it, is impossible without access to safe drinking water. Concerns over declining quality and consistency of municipal drinking water supplied to consumers have been increasing over a long time.

Effective communication lies at the heart of human connection. It helps us collaborate with each other, solve problems and build relationships. And communicating clearly is a major consideration for most of us in most aspects of life.
(MENAFN - GlobeNewsWire - Nasdaq) The Cloud ERP Market is expanding rapidly as organizations replace legacy ERP systems with scalable cloud platforms, with the U.S. market set to grow from USD 18.25 ...

For Olutoyin Green, two study abroad experiences launched a multi-semester research endeavor bridging social movements across time and space.The post Leaders From South Africa Inspire New Generation of Social Changemakers appeared first on Syracuse University Today.

On the shelf in a European supermarket, two packs of pasta sit side by side. Both claim to be "climate friendly." One carries a bright green "A" in a traffic-light scheme. The other shows a neat carbon footprint value: 1.8 kg CO2 per kg. Which one is better? Which one should you choose?
(MENAFN - PR Newswire) New data analysis clarifies misleading benchmarks released by a competitor; separate SkylineDx analysis demonstrates Merlin CP-GEP Test provides stronger metastatic-risk ...

Imagine a grain field in Western Jutland, winter wheat standing tall and golden. Now picture it being plowed up and replaced with clover grass: one of the crops intended to drive the green transition in Danish agriculture.

University of Michigan Health has launched a brain-computer interface clinic for patients with motor and speech disabilities. The health system is among the first in the nation to establish a clinic dedicated to brain-computer interfaces, which have potential to recover functionality loss that occurs due to injury or disease.

Researchers at Empa have succeeded in making aluminum-coated polymer film material even more resistant by implementing an ultra-thin intermediate layer.
ClinTrial Research (CTR) announced today that it has closed a growth equity round led by Tarsadia Investments, a multi-billion-dollar firm that makes high-conviction investments in category-defining companies globally. The investment reflects Tarsadia's conviction that CTR is positioned to become the leader in the clinical site network sector.

Windows on the Universe Center for Astronomy Outreach is a new science education and astronomy outreach center that has just opened at U.S. National Science Foundation Kitt Peak National Observatory, a Program of NSF NOIRLab.

University of Michigan researchers found a new protein target and developed a drug to treat non-small cell lung cancers that have KRAS mutations.
(MENAFN - EIN Presswire) EINPresswire/ -- The Space Situational Awareness (SSA) market is dominated by a mix of global aerospace and defense giants, specialized space technology firms, and emerging ...

CNBC’s MacKenzie Sigalos reports on Coinbase making its biggest push yet to become a one-stop financial platform, rolling out new features that expand the app into stocks, more advanced trading and prediction markets.

Researchers found a way to temporarily program cells in the liver and bolster T cell function in aging mice by compensating for the age-related decline of the thymus, where T cell maturation normally occurs. The post T Cell Populations in Aged Mice Rejuvenated By mRNA Delivery to Liver appeared first on GEN - Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology News.
(MENAFN - EIN Presswire) EINPresswire/ -- The Clinical Decision Support Systems market is dominated by a mix of global healthcare technology leaders and specialized digital health innovators. ...

An RPI team has been awarded a $3.3 million grant from the Gates Foundation to develop breakthrough purification technologies that could dramatically reduce the cost of producing mRNA-based vaccines and therapeutics.

NCAR's Mesa Laboratory is seen as a global leader in scientific research, is an economic driver and, along with other federal labs, a cultural and educational pillar in Boulder.

Lawmakers and researchers sound the alarm on the academic loophole that enables the sharing of sensitive research with China.